WIRE
Wide Field Infrared Explorer
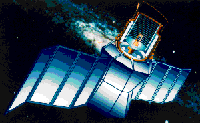 WIRE was one of two missions selected in 1994 as part of NASA's Small Explorer Program (SMEX). The spacecraft will survey the celestial sky in the infrared bands and will build on the results of the IRAS mission. The
specific objectives of the WIRE mission are to: (1) determine what fraction of the luminosity of the universe at a redshift of 0.5 and beyond is due to starburst galaxies; (2) determine whether luminous protogalaxies are common at redshifts less than 3; (3) amass a catalog larger than the IRAS Point Source Catalog; and (4) make a survey more than 500 times fainter than the IRAS Faint Source Survey at 12 and 25 µm.
WIRE was one of two missions selected in 1994 as part of NASA's Small Explorer Program (SMEX). The spacecraft will survey the celestial sky in the infrared bands and will build on the results of the IRAS mission. The
specific objectives of the WIRE mission are to: (1) determine what fraction of the luminosity of the universe at a redshift of 0.5 and beyond is due to starburst galaxies; (2) determine whether luminous protogalaxies are common at redshifts less than 3; (3) amass a catalog larger than the IRAS Point Source Catalog; and (4) make a survey more than 500 times fainter than the IRAS Faint Source Survey at 12 and 25 µm.
Spacecraft
Small Explorer bus. 3-axis stabilized, momentum biased control system with 2 arc-minutes pointing. Uses reaction wheels, gyros, star tracker, torque rods, sun-sensors. Non-articulated solar array provides 170 W
orbit average power using GaAs cells. One 9 AHr Super NiCd battery. 80386 processor with 88 MBytes memory. Uplink at 2 kbps, downlink at 18.75, 900, and 1800 kbps using 5 W S-Band transponder.
Payload
A 30 cm aperture Cassegrain telescope, diffraction limited at 25 µ m, with no moving parts or reimaging optics. Two 128 x 128 Si:As BIB focal plane arrays. Optics are cooled to less than 19 Kelvin and detectors
are cooled to less than 7.5 Kelvin using 3 kg solid hydrogen. Instrument power is 35 watts, with average data rate of 9 kbps. Each exposure lasts 32 - 128 seconds.
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Customer/User | NASA, JPL |
| Manufacturer(s) | NASA Goddard Space Flight Center |
| Launch | Planned for October 1998 on Pegasus |
| Orbit | 400 km, circular, polar, sun-synchronous |
| Design Life | 4 months |
| Related Sites | JPL WIRE Summary Page |
Information in The Mission and Spacecraft Library is provided without warranty or guarantee. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.