Wind
 Wind, and its sister spacecraft Polar, are NASA's contribution to the International Solar Terrestrial Program (ISTP), an international effort to quantify the effects of solar energy on the Earth's magnetic field. Wind will provide continuous measurement of the solar wind,
particularly charged particles and magnetic field data. This data wind will help determine how the solar wind affects magnetospheric and ionospheric behavior. The specific objectives of Wind are to: (1) provide complete plasma, energetic particle, and magnetic field input for magnetospheric and ionospheric studies; (2) determine the
magnetospheric output to interplanetary space in the upstream region; (3) investigate basic plasma processes occurring in the
near-Earth solar wind; and (4) provide baseline ecliptic planeobservations to be used in heliospheric studies. The satellite carries the first Russian instrument to fly on a US spacecraft since cooperation resumed in 1987.
Wind, and its sister spacecraft Polar, are NASA's contribution to the International Solar Terrestrial Program (ISTP), an international effort to quantify the effects of solar energy on the Earth's magnetic field. Wind will provide continuous measurement of the solar wind,
particularly charged particles and magnetic field data. This data wind will help determine how the solar wind affects magnetospheric and ionospheric behavior. The specific objectives of Wind are to: (1) provide complete plasma, energetic particle, and magnetic field input for magnetospheric and ionospheric studies; (2) determine the
magnetospheric output to interplanetary space in the upstream region; (3) investigate basic plasma processes occurring in the
near-Earth solar wind; and (4) provide baseline ecliptic planeobservations to be used in heliospheric studies. The satellite carries the first Russian instrument to fly on a US spacecraft since cooperation resumed in 1987.
Spacecraft
Body-mounted solar cells. Several long wire spin-plane antennas, inertial booms, and spin-plane appendages for instruments support sensors. Spin stabilized at 20 rpm around an axis within 1 deg of normal to the
ecliptic. Data stored using tape recorders. Downlink to Deep Space Network at 5.5 or 11.1 kbps.
Payload
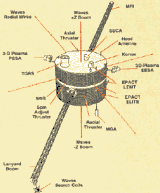
EPACT (Energetic Particle Acceleration, Composition and Transport) telescope suite - designed to provide a comprehensive study of energetic particle acceleration and transport processes in solar flares, the
interplanetary medium, planetary magnetospheres, and galactic cosmic rays. Magnetic Field Investigation (MFI) magnetometers - investigates the large-scale structure and fluctuation characteristics of the
interplanetary magnetic field as a function of time. Seven measurement ranges: plus or minus 16, 64, 256, 1024, 4096, 16,384, and 65,536 nT with resolution up to 2.5E-4 to 1 nT. Radio and Plasma Wave Experiment (WAVES) - measures the intensity and arrival direction for radio and plasma waves originating in the solar wind near the Earth. Provided by France. Solar Wind Ion Composition Spectrometer (SWICS) /
Suprathermal Ion Composition Spectrometer (STICS) - designed to provide detailed measurements of the elemental and ionic-charge composition of the solar wind, measurements of the average speed, density, and temperature of solar wind 4He++, measurements of the average speed of solar wind protons, and measurements of the energy distributions of selected ion species. Solar Wind Experiment (SWE) - a six-axis ion-electron spectrometer which provides three-dimensional velocity distribution functions for ions and electrons, with high time resolution. Transient Gamma Ray and EUV Spectrometer (TGRS) - makes
high-resolution observations of transient gamma-ray events in the energy range from 20 keV to 10 MeV. 3-D plasma and energetic paricle analyzer (3DP) - measures the three-dimensional distribution of plasma and
energetic electrons and ions with high energy, angular, and temporal resolution, over the energy range 10 eV to 5 MeV. KONUS gamma ray detectors.
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Customer/User | NASA, GSFC |
| Manufacturer(s) | Martin Marietta |
| Size | 2.4 m dia. x 2 m tall |
| Orbit | 18,000 x 990,000 miles. A figure eight, maintained using the Moon's gravitational field. After 2 years, Wind is maneuvered into a halo orbit at L1 (~1 million miles from Earth). |
| Design Life | 3 years |
| Related Sites | Wind at NDSCC |
Launch Facts
| Name | Int'l Desig. | Date | Site | Vehicle | Orbit | Mass(kg) |
| Notes | ||||||
| Wind | 1994-071A | 11/1/94 | ESMC | Delta 2 | Solar ? | 1195 |
| Solar wind research in L-1 halo orbit; part of International Solar Terrestrial Physics program | ||||||
Information in The Mission and Spacecraft Library is provided without warranty or guarantee. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.