NEAR
Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous
Part of the Discovery program
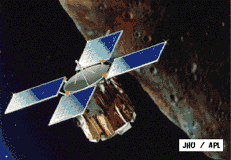 The NEAR mission is the first launch in NASA's Discovery Program, and will be the first spacecraft ever to orbit an asteroid. The mission will help answer fundamental questions about the nature and origin of near-Earth objects, as well as provide clues about the how Earth itself was formed. The vehicle will rendezvous with the asteroid 433 Eros in December 1998, and will perform up-close observations for about one year. The primary scientific goals are to measure the asteroid's: (1) bulk properties (size, shape, volume, mass, gravity field, and spin state); (2) surface properties (elemental and mineral composition, geology, morphology, and texture); and (3) internal properties (mass distribution and magnetic field). Prior to its encounter with Eros, NEAR will also fly by the Main Belt asteroid Illya.
The NEAR mission is the first launch in NASA's Discovery Program, and will be the first spacecraft ever to orbit an asteroid. The mission will help answer fundamental questions about the nature and origin of near-Earth objects, as well as provide clues about the how Earth itself was formed. The vehicle will rendezvous with the asteroid 433 Eros in December 1998, and will perform up-close observations for about one year. The primary scientific goals are to measure the asteroid's: (1) bulk properties (size, shape, volume, mass, gravity field, and spin state); (2) surface properties (elemental and mineral composition, geology, morphology, and texture); and (3) internal properties (mass distribution and magnetic field). Prior to its encounter with Eros, NEAR will also fly by the Main Belt asteroid Illya.
Spacecraft
3-axis stabilized. 4 deployed, non-articulating fixed solar panels provide 1600 watts at 1 AU. Fixed 1.5 m diameter high gain antenna. X-band communications using via DSN with selectable data rates between 1 and 27 kbps. Passive thermal control. 1 Gbit solid state data storage. Hydrazine propulsion system with one 100 lbf, four 5 lbf, and seven 1 lbf thrusters provide a total delta-V of 1425 m/s.
Mission control provided by JHU APL with navigation support from JPL.
Payload
The instrument payload totals 55 kg and 48 watts. MultiSpectral Imager (MSI) - a refractive
telescope with passively cooled Si CCD array (244 x 537) that will determine the overall size, shape, and spin characteristics of the asteroid, map the morphology and composition of the surface, and search
for satellites of Eros. 2.25 x 2.9 deg FOV, 10-16 meter resolution from 100 km altitude, sensitive between 400 and 1100 nm. X-Ray/Gamma-Ray Spectrometer (XGRS) - containing two sensors (an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer and a gamma-ray spectrometer), XGRS will be used to determining the surface/near-surface elemental composition of the asteroid. Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIS) - a spectrometer covering 800-2700 nm, NIS is designed to map the mineralogic composition of Eros. Magnetometer - a three-axis fluxgate sensor that will be used to measure Eros' magnetic field. These measurements will help determine the internal composition of the asteroid. NEAR Laser Rangefinder (NLR) - an altimeter that uses a solid-state pulsed laser to measure the distance between the spacecraft and the surface of the asteroid. It will be used to make will make accurate measurements of the asteroid's shape and detailed surface structure. Nd-YAG laser
operating at 1.064 mm wavelength, 6 meter resolution, 50 km range. Radio Science - uses the satellite's telemetry system to map Eros' gravity field.
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Customer/User | NASA |
| Manufacturer(s) | JHU/APL |
| Size | 1.7 x 1.7 x 2.75 meter |
| Orbit | Variable, ranging from 1000 x 1000 km to 35 x 35 km about Eros - 2 year Delta-V Earth Gravity Assist / Asteroid Illya flyby: August 1996 / Earth flyby: January 1998 / Asteroid Eros rendezvous: December 1998 |
| Design Life | 4 years |
| Related Sites | NEAR Home Page |
Launch Facts
| Name | Int'l Desig. | Date | Site | Vehicle | Orbit | Mass(kg) |
| Notes | ||||||
| NEAR | 1996-008A | 2/17/96 | ESMC | Delta 2 | Solar | 818 |
| Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous; 1st Discovery mission; will orbit asteroid Eros for extended observations | ||||||
Information in The Mission and Spacecraft Library is provided without warranty or guarantee. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.