MSX
Midcourse Space Experiment
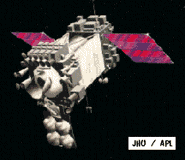 The MSX observatory is a BMDO sponsored mission designed to demonstrate a variety of multispectral imaging technologies to identify and track ballistic missiles during flight. In addition, it will perform scientific investigations of the composition and dynamics of the Earth's atmosphere by observing ozone, chloroflourocarbons, carbon dioxide and methane. Spacecraft cost is estimated at $325M.
The MSX observatory is a BMDO sponsored mission designed to demonstrate a variety of multispectral imaging technologies to identify and track ballistic missiles during flight. In addition, it will perform scientific investigations of the composition and dynamics of the Earth's atmosphere by observing ozone, chloroflourocarbons, carbon dioxide and methane. Spacecraft cost is estimated at $325M.
Spacecraft
3-axis stabilized to 0.01 deg using reaction wheels with knowledge to 9 µ rad (post-processed). 108 Gbits data storage. Steerable X-band antennas with 2 kbps uplink and downlink up to 25 Mbps. Dual
solar arrays (single-axis articulation) provide 1200 W BOL. NiH2 batteries.
Payload
The instruments consist of 11 optical sensors making observations at a wide range of infrared, visible and ultraviolet wavelengths from 110 nm to 28 µ m. Primary instruments: SPIRIT III (Space Infrared Imaging Telescope), UVISI (Ultraviolet and Visible Imagers and Spectrographic Imagers), SBV
(Space-Based Visible instrument), OSDP (On-board Signal and Data Processor), and reference objects (2 cm spheres to be deployed from MSX).
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Customer/User | BMDO |
| Manufacturer(s) | JHU/APL |
| Size | 1.5 x 1.5 x 5.1 meters |
| Orbit | 900 km, high inclination, circular, near-sun-synchronous |
| Design Life | 4 years (with 18-20 months of coolant for IR sensors), 5 year goal |
Launch Facts
| Name | Int'l Desig. | Date | Site | Vehicle | Orbit | Mass(kg) |
| Notes | ||||||
| MSX | 1996-024A | 4/24/96 | WSMC | Delta 2 | LEO | 2700 |
| Midcourse Space eXperiment; missile detection technology tests; also used for auroral and atmospheric studies | ||||||
Information in The Mission and Spacecraft Library is provided without warranty or guarantee. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.