Mariner 5
Part of the Mariner program
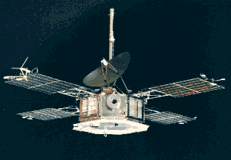 Mariner 5 carried a complement of experiments to probe Venus's atmosphere with radio waves, scan its brightness in ultraviolet light, and sample the solar particles and magnetic field fluctuations above the planet. It flew by Venus on October 19, 1967 at an altitude of 3,990 kilometers. With more sensitive instruments than its predecessor Mariner 2, Mariner 5 was able to shed new light on the hot, cloud-covered planet and on conditions in interplanetary space. Operations of Mariner 5 ended in November 1967.
Mariner 5 carried a complement of experiments to probe Venus's atmosphere with radio waves, scan its brightness in ultraviolet light, and sample the solar particles and magnetic field fluctuations above the planet. It flew by Venus on October 19, 1967 at an altitude of 3,990 kilometers. With more sensitive instruments than its predecessor Mariner 2, Mariner 5 was able to shed new light on the hot, cloud-covered planet and on conditions in interplanetary space. Operations of Mariner 5 ended in November 1967.
Spacecraft
Octagonal bus structure with four solar panels. 3-axis stabilized using cold gas thrusters. S-Band communications via LGA and HGA. Thermal shield.
Payload
Instruments examined Venus' atmosphere with radio waves and ultraviolet scanners and sampled the solar particles and magnetic fields in the region of the planet.
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Customer/User | NASA |
| Manufacturer(s) | JPL |
| Orbit | Solar orbit - Flyby trajectory. Arrival at Venus on October 19, 1967. |
| Related Sites | JPL Mariner 5 Summary |
Launch Facts
| Name | Int'l Desig. | Date | Site | Vehicle | Orbit | Mass(kg) |
| Notes | ||||||
| Mariner 5 | 1967-060A | 6/14/67 | ESMC | Atlas Agena D | Solar | 244 |
| Venus flyby 10/19/67 | ||||||
Information in The Mission and Spacecraft Library is provided without warranty or guarantee. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.