Magellan
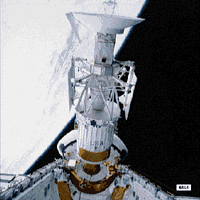 Magellan was designed to develop an understanding of the geological structure of Venus, including its density distribution and dynamics. During its 4 year orbital tour (1990-1994), Magellan (named after the Portugese explorer who first circumnavigated the Earth) provided detailed topographic maps of Venus' surface using a synthetic aperture radar to penetrate the planet's thick cloud cover. The radar imaged 98 percent of the surface with a resolution of 100 m. Additional studies included measurements of surface altitude using radar altimetry and measurements of the planet's gravitational field using precision radio tracking. At the end of its useful life, Magellan was commanded into a gradual dive into the Venusian atmosphere to obtain information about its properties, where it finally burned up on Oct. 12, 1994.
Magellan was designed to develop an understanding of the geological structure of Venus, including its density distribution and dynamics. During its 4 year orbital tour (1990-1994), Magellan (named after the Portugese explorer who first circumnavigated the Earth) provided detailed topographic maps of Venus' surface using a synthetic aperture radar to penetrate the planet's thick cloud cover. The radar imaged 98 percent of the surface with a resolution of 100 m. Additional studies included measurements of surface altitude using radar altimetry and measurements of the planet's gravitational field using precision radio tracking. At the end of its useful life, Magellan was commanded into a gradual dive into the Venusian atmosphere to obtain information about its properties, where it finally burned up on Oct. 12, 1994.
Spacecraft
3-axis stabilized using 3 reaction wheels. A 3.7 m diameter high gain antenna was used for both telecommunications and radar. Attitude sensors include 2 cruise sun sensors, 1 star scanner, and 2 inertial reference units. Power system included a 12.5 m2 solar array (1029 W EOL) and NiCd batteries (2 x 30 AHr). Hydrazine propulsion system with 0.9N, 445 N thrusters. X-band (20 W) and S-Band (5 W) communications. Downlink rates of 268.8 or 115 kbps. Uplink rates of 31.25 and 62.5 bps.
Payload
A single radar instrument operated simultaneously as a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR), altimeter, and radiometer. Radar frequency 2.385 GHz, with 325 W peak power and 25 km swath width (variable). Altimeter resolution 30 m. Radiometer accuracy 2 deg C. SAR resolution 150 m (range and azimuth).
An X- and S- band radio subsystem precisely tracked the spacecraft's orbit to make measurements of the gravity field.
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Customer/User | NASA, JPL |
| Manufacturer(s) | Martin Marietta |
| Size | 6.4 m long by 9.2 m across |
| Orbit | 15 month trip including one and a half loops around the Sun / Entered Venus orbit August 10, 1990. 310 x 8890 km, incl. = 86 deg. Period = 3.25 hrs |
| Design Life | 4 years |
| Related Sites | JPL Magellan Summary Page |
Launch Facts
| Name | Int'l Desig. | Date | Site | Vehicle | Orbit | Mass(kg) |
| Notes | ||||||
| Magellan | 1989-033B | 5/4/89 | ESMC | STS 30 | Venus | 3444 |
| Deployed from STS-30 5/5/89; entered Venus orbit 8/10/90; SAR imaging of planet surface, gravitational field mapping | ||||||
Information in The Mission and Spacecraft Library is provided without warranty or guarantee. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.