GRO
Compton Gamma Ray Observatory
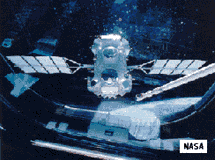 CGRO is the gamma-ray element of the Great Observatories program (along with HST (visible), AXAF (X-ray), and SIRTF (infrared)). The spacecraft carries 7 tons of instruments to detect, image and analyze gamma rays emitted by cataclysmic cosmic events. CGRO will help address fundamental questions about the process of energy transfer in the universe and lead to a better understanding of the nature of astronomical objects that produce this very high-energy radiation. The specific objectives of the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory include (1) studying gamma-ray sources emitting in our
Galaxy and beyond, (2) investigating evolutionary forces in neutron stars and black holes, (3) performing detailed studies of nucleosynthesis, and (4) searching for primordial black hole emissions. The program includes participation from Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and ESA.
CGRO is the gamma-ray element of the Great Observatories program (along with HST (visible), AXAF (X-ray), and SIRTF (infrared)). The spacecraft carries 7 tons of instruments to detect, image and analyze gamma rays emitted by cataclysmic cosmic events. CGRO will help address fundamental questions about the process of energy transfer in the universe and lead to a better understanding of the nature of astronomical objects that produce this very high-energy radiation. The specific objectives of the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory include (1) studying gamma-ray sources emitting in our
Galaxy and beyond, (2) investigating evolutionary forces in neutron stars and black holes, (3) performing detailed studies of nucleosynthesis, and (4) searching for primordial black hole emissions. The program includes participation from Germany, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and ESA.
Spacecraft
3-Axis stabilized, zero momentum biased control system using reaction wheels. Two solar array generate 4500 W (BOL) power. Three 50 Ahr NiCd batteries. Hydrazine propulsion system (1900 kg fuel) with four 100-lbf thrusters and eight 5-lbf ACS thrusters. S-band telecom system using
1.52 m HGA on a 4.4 m boom provides uplink at 1 kbps and downlink (via TDRSS) at 256-512 kbps. GRO is the first spacecraft designed for on-orbit refueling, servicing and maintenance.
Payload
Four instruments are carried. OSSE (Oriented Scintillation Spectrometer Experiment) by Naval Research Laboratory detects gamma rays entering the field of view of any of four detectors in the 100 kev to 10 Mev range. The Imaging Compton Telescope by Max Planck Institute is tuned to the 1-30 Mev energy range and determines the angle of arrival within a degree and the energy of photons
to within five percent at higher energies. The Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET) measures high energy (20 Mev to 30 gev) gamma ray source positions to a fraction of a degree and photon energy to within 15 percent. EGRET is developed by NASA GSFC, Max Planck Institute, and Stanford University. The Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE) by NASA MSFC
scours the sky to short duration gamma ray bursts (20 to 600 kev) and conducts full sky surveys for long lived sources.
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Customer/User | NASA, GSFC |
| Manufacturer(s) | TRW |
| Size | 4.6 m x 9.1 m, solar arrays span 21.3 m |
| Orbit | 450 km circular, 28.5 deg inclination |
| Design Life | 2.25 years w/8 yrs fuel |
| Related Sites | CGRO Science Support Center |
Launch Facts
| Name | Int'l Desig. | Date | Site | Vehicle | Orbit | Mass(kg) |
| Notes | ||||||
| GRO | 1991-027B | 4/5/91 | ESMC | STS 37 | LEO | 15620 |
| Astrophysical laboratory for gamma ray observations; deployed from STS-37 4/7/91; renamed Compton Gamma Ray Observatory | ||||||
Information in The Mission and Spacecraft Library is provided without warranty or guarantee. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.