GFO
GEOSAT Follow On
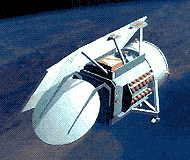 GFO is a follow-on to the successful GEOSAT program which flew between 1985 and 1990. GFO will provide real-time ocean topography data to 65 Navy users at sea and on shore. This data on wave heights, currents and fronts will also be archived and made available to scientific and commercial users through NOAA. The GFO contract was awarded in September 1992 and is worth $46M for the first satellite and $115M if options for two additional spacecraft are exercised. These costs include launch, ground software and 60 days operation. Contract includes incentive fees based on long-term on-orbit performance.
GFO is a follow-on to the successful GEOSAT program which flew between 1985 and 1990. GFO will provide real-time ocean topography data to 65 Navy users at sea and on shore. This data on wave heights, currents and fronts will also be archived and made available to scientific and commercial users through NOAA. The GFO contract was awarded in September 1992 and is worth $46M for the first satellite and $115M if options for two additional spacecraft are exercised. These costs include launch, ground software and 60 days operation. Contract includes incentive fees based on long-term on-orbit performance.
Spacecraft
3-axis stabilized. Single solar array with 1-axis articulation. Hydrazine propulsion system for orbit maintenance. Redundant GPS receivers provide precision orbit determination with an rms accuracy (radial component) of 10 cm. A doppler beacon transmitter is also carried to support orbit
determination.
Payload
A radar altimeter is the primary payload. This 13.5 GHz radar provides 3.5 cm height measurement precision. The other payload is a dual frequency (22 and 37 GHz) water vapor passive radiometer with a path correction accuracy of 1.9 cm rms. Total payload is 47 kg and 121 watts.
| Country of Origin | United States |
| Customer/User | US Navy |
| Manufacturer(s) | Ball Space Systems, E-Systems |
| Size | 3 m long |
| Launch | Planned for September 1996 on Taurus |
| Orbit | 880 km circular, 108 deg inclination, 17 day repeat |
| Design Life | 8 years |
| Related Sites | GFO Validation Page |
Information in The Mission and Spacecraft Library is provided without warranty or guarantee. USE AT YOUR OWN RISK.